Varieties
Single Mogra, Double Mogra, Iruvatchi, Ramanathapuram local and Arka Aradhana etc. are presently cultivated. ab
 |
| Single Morga |
Double Morga |
Soil and climate
Well drained loamy or red loamy fertile soil. Warm summer, mild winter, moderate rainfall and sunny days.
Propagation: Semi hard wood cuttings (15 - 20 cm long).
Preparation and planting
Layers or rooted cuttings are planted in pits 30 x 30 x 30 cm with a spacing of 1.25 m either way to accommodate 6400 plants per ha during June to November. 20 kg FYM/pit is applied before planting.
Irrigation
Irrigation should be given immediately after planting followed by weekly irrigation depending upon weather conditions.
Manuring
FYM @ 10 kg/pit is applied before planting. NPK @ 60:120:120 g/plant/year is applied in 2 equal splits during November (after pruning) and June-July along with 10 kg FYM per plant.
Micronutrients
Foliar spray ofZnSO40.25% + MgSO40.5% + FeSO40.5% (In case of expression of micronutrient deficiency, spraying should be done at fortnightly intervals until the chlorotic symptoms disappear).
Pruning
The bushes are pruned to 50 cm height from the ground level during last week of November. Plant protection
Pests
A number of insect pest attack jasmine crop and cause considerable damage. Among them the most important ones are the bud worm (Hendecasis duplifascialis),leaf webber (Nausinoe geometralis) and the blossom midge (Contarinia maculipennis) and recently the mite (Tetranychus urticae) attack due to prevailing drought and hot weather. Among the different insect pests recorded, bud worm are known to poses a serious threat to flower production.
Budworm - Hendecasis duplifascialis
Damage symptom
Hendecasis duplifascialis larvae cause greatest injury to immature buds of Jasminum sambac. The larvae found inside the bud or in flower cluster feeding on buds. It feeds on the inner most petals of the closed bud in the initial stages, emerged through a circular hole made on the tubular portion of the corolla for tunneling into the other buds in the same shoot and pupates in the soil. The larvae makes tunnels of silk and excreta within an affected flower cluster, thus affecting the flower opening and flower buds may drop off and finally the flower buds changes into pinkish colour.
 |
 |
 |
| Bore holes on bud |
caterpillars seen inside the bud |
Infested flower |
 |
 |
| Colour of buds changes to pink |
|
Control measures
- Spray Thiochloprid (Alanto) 240SC 1 ml/litre or Spinosad (Tracer) @ 0.5 ml/lit
- Spray Profenophos 25EC @ 2 ml/lit
- Spray neem seed kernel extract 5 %
- Spray Bacillus thuringiensis 2 g/litre
- Set up four Helilure sex pheromone trap per acre
Leaf webber – Nausinoe geometralis:
Damage symptom
The damage caused by Nausinoe geometralis , the caterpillar built elaborate network of webbing of leaves, especially in the lower portion causing severe injury. Caterpillar feeds on the leaves by scrapping the chlorophyll. The lower foliage is infested during the rainy days. The infestation severe in terminal shoots during dry and sunny weather. The larvae had shorter developmental period during September – December on J. sambac and the 3rd and 4th instars were found to be destructive causing heavy damage to the foliage.
 |
 |
| Webbing on leaves |
Leaf Webber on leaves |
Control measures
- Imidacloprid 2ml/lit or Dimethoate 2 ml per lit gives season long systemic control
- Acetamiprid 20P @ 80 g ai./ha or neem oil @ 3 ml/l of water
- Yellow-orange sticky traps @ 5/acre can be used to monitor whitefly numbers
- Insecticidal soaps or neem oil may reduce populations
- General predators include Green lacewings, Scymnus and Chrysoperla oculata.
Blossom midge (Contarinia maculipennis):
Damage symptom
The maggots of the blossom midge enter into the buds at the base of the corollas which results in swelling at the base of the buds. The infestation leads to stunting and drying of plants or leads to stunted growth and ultimately drying of plants.
 |
 |
| Webbing on leaves |
Leaf Webber on leaves |
Control measures
- Spray Thiamethoxam 2.5% WG @ 0.75 g/litre or Flufenoxuron @ 1.5 g/lit.
- Spraying of Rynaxypyr @ 0.5ml/litre or Novaluron 3ml/lit. of water.
Eriophyid mite - Aceria jasmine:
Damage symptom
Inter cropping by using host-non-host crops. It infests the leaf surface, tender stems and buds. It produces velvet like hairy growth on the leaf surface. The growth of plant is stunted and flower production is suppressed.
Control measures
- Use NSKE and other botanicals
- Avoid using synthetic pyrethroids
- Fenazaquin (Magister) 10 EC @ 2ml/litre
- Abamectin or Exodus 0.5 ml /litre.
Diseases
Yellowing of leaves
It is caused by 3 factors viz., iron deficiency, nematode infection and root rot disease.
Iron deficiency
It can be rectified by spraying Ferrous sulphate 5 g/lit at monthly intervals until the chlorotic symptoms disappear.
Nematode
Initially test the soil for nematode infection. Apply 10 g of of Phorate granules near root zone and then irrigate the field.
Root rot
Drench the soil around the plant with Copper oxychloride at 2.5 g/lit.
Soil drenching with Trifloxystrobin + Tebuconazole @ 0.75 g/litre or Difenoconazole @ 0.5g/l.
Alternaria leaf spot
Foliar application of Mancozeb @ 2.5 g/l or Azoxystrobin @ 1g/l
Soil application of Pseudomonas fluorescens @ 25 g/m2 and foliar application of P. fluorescens @ 5 g/l at monthly intervals after planting.
Season of flowering and harvest
Flowering commences in March - April. Fully developed unopened flower buds should be picked in the morning hours.For concrete extraction, fully opened flowers are harvested.
Yield
Flowers: 8 - 9 t/ha; concrete recovery: 0.14 - 0.19%.
Value addition
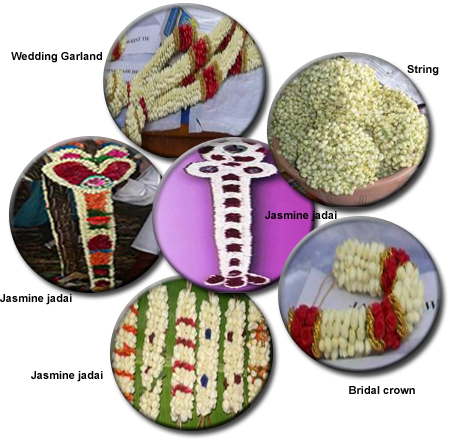
Jasmine is one of the most important traditional flower of India. Jasmine flowers buds are used for making garland, bouquets, string, veni and jadai for grand hair dressing of women on special occasions. Extraction of essential oil from jasmine for preparing perfume, hair oils and attar.
Wedding Garlands
The wedding garland made of jasmine flower buds are predominant than garlands made from other flowers because of its special fragrance and manifestation
String
Women of all age groups need adorn their hair with flower string. Mostly jasmine strings are liked by women folk as it adds to their beauty.
Bridal crown
Crowns made of mostly jasmine flower buds are used in some marriages for adorning the couple.
Jasmine jadai
It is also a decorative items necessarily used for hair dressing of the bride during marriages.
Hand wrist
Which is made by jasmine buds, Nandhiyavattam and rose petals
Tinting
Tinting is the technique which is used for making colouring of flowers. While making garlands, strings, veni, jadai etc., tinting of jasmine is also done for getting varied designs.
Packing Jasmine for local market

Special Packing for Export (Dubai) (New York)
Precision production technology
Main field preparation: Ploughing with chisel, disc, rotovator and cultivator and levelling with tractor drawn leveller. Pits of 45cm3 size are dug.
Spacing: 1.2 x 1.0 m (8333 plants/ha).
Herbicide application: Pre emergence application of Pendimethalin @ 2ml/l.
Biofertilizers: Soil application of2 kg each of Azospirillum and Phosphobacteria per ha at the time of planting. It is to be mixed with 100kg of FYM and applied in pits.
Media consortia: 5kgFYM + 500g Neem cake + 100g Vermicompost are applied per pit at the time of planting.
Irrigation: Once in 3 days through drip system.
Fertigation: 100% RDF (60:120:120g NPK/plant/year) as WSF [Polyfeed (19:19:19), Potassium Nitrate (13:0:45) and Urea].
Biostimulants: Foliar spray of Panchagavya 3% + Humic acid 0.4% at monthly intervals.
Micronutrients: Foliar spray of FeSO4@ 0.5% + ZnSO4 @0.5% at monthly intervals.
Yield: 12 t/ha.
Source
-
http://farm1.static.flickr.com/225/489187967_e490b37b79.jpg
-
http://www.nzenzeflowerspauwels.be/JasmSamb.jpg
-
www.toptropicals.com/html/toptropicals/catalog/ph
-
http://farm2.static.flickr.com/1426/1170785933_17e9c4bf75.jpg?v=0
- http://www.naiptnauflowers.com/ValueAddition.php
|